Unleashing the Power of Data: The Competitive Edge for Private Markets
April 25, 2023
This post is the first in a four-part series titled "Unleashing the Power of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Building Your Private Markets Data Strategy" that explores the importance of having a data strategy framework for private markets and why it is a topic of growing interest, published by Lionpoint’s Front & Middle Office team
Introduction
Data-driven decision-making is essential in today’s business environment, where investment managers must operate with agility and respond quickly to changing market conditions. Leveraging data as a vital, differentiating asset, is crucial for organizations to uncover opportunities and optimize operational efficiency. Within private markets, firms that have a clear data strategy are best positioned to capitalize on their data and wield information as a source of competitive advantage.
In this series, we plan to dive into the components that drive an effective data strategy. We will begin by defining data strategy and introducing its key concepts.
Do you know your data management maturity score? Make sure you complete the Data Management Strategy Questionnaire at the end of this post.
Future posts will include:
- Part 2 – Building a Foundation: Defining a Best-in-Class Data Strategy Operating Model. Review foundational elements of a best-in-class operating model for an enterprise data strategy. Elements include defining a Data Estate, performing a Data Operation Assessment, performing a Data Architecture Assessment, and designing a Target State Operating Model.
- Part 3 – Putting the Plan into Action: Executing a Data Strategy Program. Highlight the benefits of implementing a data strategy, identify common complexities of an implementation, and detail best-practice implementation elements and methodologies.
- Part 4 – Sustaining Success: Maintaining a robust Data Strategy. Define the benefits of data strategy-as-a-service and identify the value-add of ongoing data strategy and data operations support.
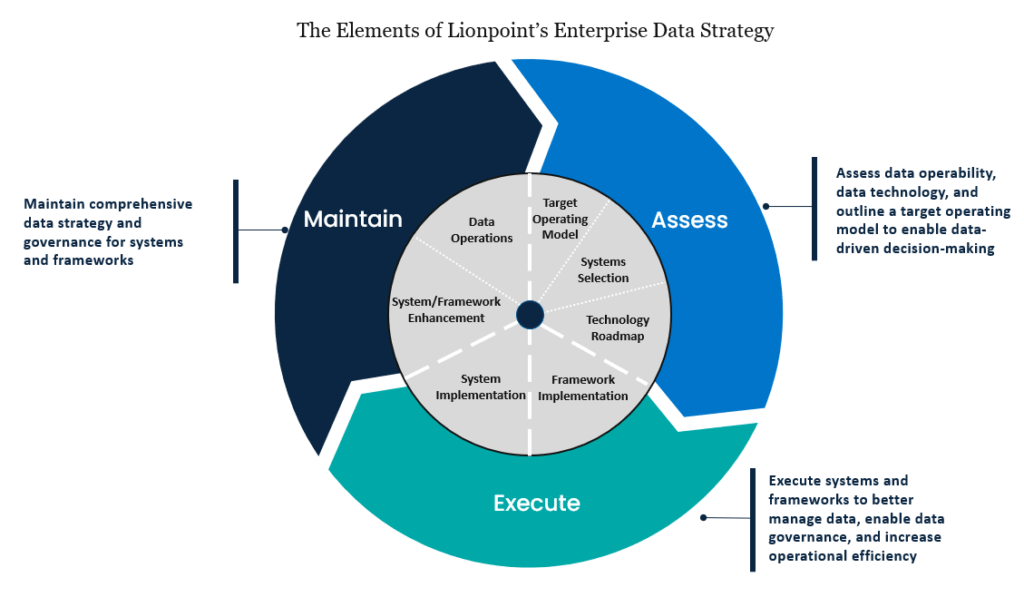
The Competitive Advantage of a Well-Defined Data Strategy
Data strategy is a comprehensive plan that defines how an organization will acquire, manage, and use its information assets to achieve business goals. Data strategy frameworks provide guiding principles that encompass the processes, people, and technology related to data management across an organization. Elements of a data strategy include data governance, data quality assessment, data analytics, and data security.
A well-defined data strategy can create a competitive advantage in several ways:
- Increased operational efficiency. A data strategy enables increased efficiency through better resource utilization and reduced costs, leading to streamlined operations, improved margins, and a greater return on investment.
- Improved investor experience. General Partners (GPs) with a focused data strategy can better understand their portfolio companies and rapidly assess potential investments by facilitating due diligence and sharpening post-investment analysis. Additionally, leveraging data to tell a compelling story to Limited Partners (LPs) increases the likelihood of recurring commitments.
- Overall competitiveness. Analytics support informed decisions using accurate and timely data. A data strategy that leverages comprehensive data across functional teams is more likely to generate portfolio company insights and drive value creating innovation.
- Better Risk Management. By analyzing data and identifying potential risks, GPs can develop strategies to mitigate those risks. This can lead to a competitive advantage in terms of risk management and resilience.
Data Strategy Trends
The state of data strategy today is evolving rapidly as investment managers explore new ways to capitalize on their data and drive business outcomes. Organizations of all sizes can benefit from investing in their data capabilities. Some prevailing trends include:
- Migration to cloud-based technologies. Enterprise cloud infrastructure optimizes application capabilities and solutions development by quickly scaling up to meet business needs. Leaders in cloud transformation can leverage machine learning and AI capabilities while exploring monetization opportunities through valuable internal data or proprietary apps.
- Greater emphasis on data governance. With more data at their disposal, organizations have begun investing in data governance by defining processes and policies to manage data securely. Investment managers must also adhere to the rapidly evolving regulatory environment by bolstering their compliance measures.
- Increased investment in data quality. Investment into data quality reflects a growing recognition of the importance of data quality, and the need for organizations to adopt new approaches and technologies to ensure the quality of their data. By monitoring data quality and taking action to address issues, organizations can improve decision-making, reduce risk, and achieve better outcomes.
- Data as an asset. For an insights-driven organization, harnessing the power of data can unlock competitive advantages, especially within operations. Centralized, simplified, and easily-accessible data enables the business intelligence and technical flexibility required to monetize data and support business objectives.
- Proliferation of AI and machine learning. With the availability of large amounts of data and advances in technology, businesses increasingly use AI and machine learning to analyze data, automate tasks, and gain insights. This includes using natural language processing, predictive modeling, and image recognition.
Common Complexities
Implementing a data strategy can be a complex undertaking for any organization. While the benefits of data-driven decision-making are clear, many technical challenges and organizational hurdles can arise when developing and implementing a data strategy. In this context, it is important for businesses to understand the common complexities of implementing a data strategy and to develop frameworks that overcome these challenges. By doing so, businesses can ensure that they are able to leverage the full potential of their data and achieve their strategic goals. Below are common complexities in the industry:
- Organizational culture. Implementing a data strategy requires a shift in organizational culture towards a data-driven approach. Changing the status quo can be difficult, and implementing a new data quality framework may require significant organizational change, including modifications to processes, workflows, and systems.
- Data governance. Data governance involves setting up policies, procedures, and standards for managing and using data, including compliance and regulatory guidelines. Developing and implementing an effective data governance framework can be a time-consuming and expensive process.
- Data integration. Data integration involves combining data from multiple sources to create a unified view, requiring careful planning and attention to detail. Integrating data from disparate sources and across multiple workstreams poses many logistical and technological challenges. Close collaboration between executive leadership, technology, and business stakeholders is required to align the data strategy with broader business objectives.
- Data quality. Data quality assessment is a critical piece to any data strategy, as only high-quality data can drive effective decision-making. Bad data is costly, and measuring overall data quality can be ambiguous, leading to ineffective information management.
- Technology infrastructure. Executing data strategy requires a technology infrastructure that can ingest large volumes of data and support advanced analytics. GPs may need to invest in new technologies to realize their data strategy goals.
Conclusion
As private markets’ technology continues to advance, GPs will continue to accumulate more data and face increased demands for accurate and timely reporting. Developing a data strategy to meet those growing demands is crucial to any investment manager looking to maximize the utility of their data and achieve their business objectives. Partnering with the right professionals, both internally and externally, will ensure that the requisite expertise is on board to navigate the complexities of defining and implementing an effective data strategy.
From data governance to analytics and beyond, Lionpoint Group can provide the guidance and support you need to succeed in today’s data-driven world. Take the first step towards improving your organization’s data management practices by completing Lionpoint’s Data Management Questionnaire and contact us to learn more about how we can be a partner who can help you unlock the full potential of your data and achieve your strategic objectives. Contact: Miguel Castaneda at mcastaneda@lionpointgroup.com