Unleashing the Power of Data: Putting the Plan into Action
June 07, 2023
Editor's Note: This post is the third in a four-part series titled "Unleashing the Power of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Building Your Private Markets Data Strategy" that explores the importance of having a data strategy framework for private markets and why it is a topic of growing interest, published by Lionpoint’s Front & Middle Office team.
Previous posts outlined the importance of formulating a target operating model, choosing a system, and assessing data frameworks. In this post, we will dive into the elements of executing a data strategy program, highlight the benefits of implementing a data strategy, identify common complexities of an implementation, and detail best-practice implementation elements and methodologies.
Introduction
In today’s business landscape, data strategy implementation has become a crucial driver of success. Organizations are recognizing the transformative power of effectively managing and utilizing data. In this third-part of our four-part series on Enterprise Data Strategy, we explore the numerous benefits of implementing a data strategy. From improved decision-making to operational efficiency, a well-executed data strategy can revolutionize organizations. We discuss the advantages of system implementation, enabling data processing and analysis, and framework implementation, providing a roadmap for data governance. We also address challenges such as change management, resource constraints, data quality, and system integration. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge to unlock your data’s potential and gain a competitive edge.
Benefits of Data Strategy Implementation
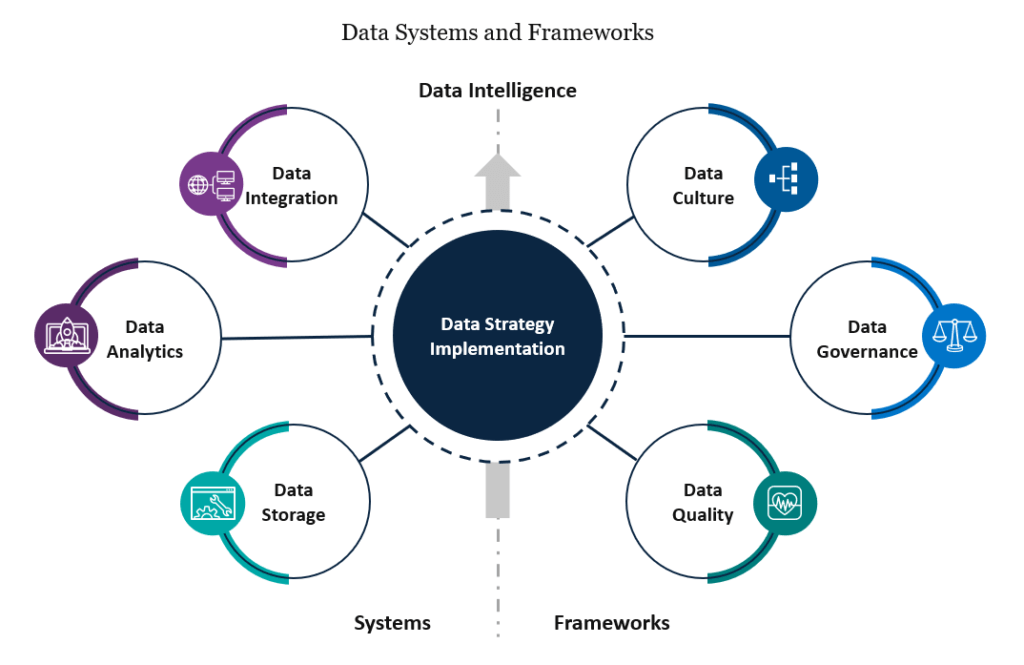
Implementing a data strategy can bring numerous benefits to organizations, revolutionizing their operations and empowering them to make informed decisions. The advantages of data strategy implementation can be categorized into two key areas: system implementation and framework implementation.
- System Implementation. Integrating a new data technology solution, such as a data warehouse or business intelligence tool, provides organizations with the necessary infrastructure to process and analyze data effectively. This upgrade is particularly significant for private market investors who have traditionally relied on Excel spreadsheets. By transitioning to a more robust analytics platform, organizations can experience immediate improvements in their data management processes. Excel processes are limited in scalability, but with the right tools in place, efficiency is enhanced, costs are reduced, and risks associated with data management are mitigated. Organizations gain the ability to process data at scale, uncover valuable insights, and leverage data as a strategic asset for growth and competitiveness.
- Framework Implementation Frameworks serve as playbooks that guide organizations through the intricacies of change management, data governance, and data quality measurement. By incorporating a framework into their data strategy, organizations can streamline their data operations and reduce overhead. The consistent application of a well-designed framework allows organizations to manage data efficiently, regardless of its source. This approach enhances accessibility, reduces the time and effort spent on data retrieval, and enables users to focus on analysis rather than struggling with data-related challenges. Furthermore, a framework introduces transparency and rigor into data management processes, maximizing the utility of data for generating insights and enabling better reporting.
Common Complexities
Implementing a data strategy can be a complex endeavor, requiring careful consideration of various factors. While the benefits are significant, organizations must be prepared to navigate the following common complexities:
- Change management. Implementing a data strategy often involves introducing new processes and technologies, which can lead to a significant shift in an organization’s culture and workflows. This change may be met with resistance from employees who are accustomed to existing practices. Effective change management involves close coordination among management, technology teams, and business units to ensure engagement and foster a sustainable transformation. A holistic approach that involves clear communication, training, and support is crucial to overcome resistance and drive adoption.
- Resource constraints. Implementing a data strategy requires substantial investments in terms of finances, time, and human resources. Organizations, especially those with lean operations, may face challenges in allocating the necessary capacity or budget to execute their data strategy effectively. To address this complexity, careful resource planning, prioritization, and leveraging external expertise or partnerships can help optimize resource utilization and ensure the successful implementation of the data strategy.
- Data quality. The success of a data strategy heavily relies on the quality of the data being used. Poor data quality can be costly and hinder the effectiveness of data-driven initiatives. Incorporating data quality assessment into the framework is essential to avoid data quality issues. Organizations should establish data quality standards, perform regular data quality checks, and implement processes to address and rectify data quality issues. By maintaining high data quality standards, organizations can ensure the reliability and trustworthiness of their data assets.
- System integration. Organizations often have complex technology ecosystems with legacy systems and a diverse range of technologies in place. Integrating new data technologies and ensuring compatibility with existing systems can be a complex undertaking. Organizations need to conduct thorough due diligence before selecting software solutions, consider factors such as interoperability and scalability, and engage external experts if necessary to facilitate a seamless integration process. A well-planned integration strategy, including data mapping, system testing, and data migration, is essential to ensure smooth operations and minimize disruption during the implementation.
Methodology of Implementing a Data Strategy Program
Implementing a data strategy requires a systematic approach to ensure successful outcomes and maximize the benefits for an organization. The implementation methodology can be divided into two categories: system implementation and framework implementation.
System Implementation Methodology:
- Define Business Objectives: Clearly articulate the business objectives and requirements that the new data technology solution aims to address. This includes identifying key performance indicators, data processing needs, and desired outcomes.
- Evaluate and Select Solutions: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of available data technology solutions in the market. Consider factors such as functionality, scalability, interoperability, and vendor support. Choose a solution that aligns with the organization’s business objectives and can meet its specific data processing and analysis requirements.
- Plan and Design: Develop a detailed plan for the implementation process, including project scope, timelines, resource allocation, and milestones. Collaborate with stakeholders and end-users to gather their input and ensure that the system design meets their needs. Design the system architecture, data models, and integrations to optimize performance and data flow.
- Configuration and Development: Configure the selected data technology solution based on the organization’s requirements and best practices. This may involve customizing the solution, defining data workflows, and integrating it with existing systems. Develop any necessary data pipelines, transformations, or data cleansing processes to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Conduct rigorous testing across different environments and scenarios to ensure the system functions as intended. Validate data accuracy, system performance, and user experience. Engage stakeholders and end-users to gather feedback and address any identified issues. Iterate and refine the system configuration as necessary.
- Deployment and Training: Deploy the system in a controlled manner, considering data migration, cutover plans, and user access controls. Provide comprehensive training materials and conduct user training sessions to familiarize stakeholders and end-users with the new system. Support users during the transition period to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth adoption process.
Framework Implementation Methodology:
- Define Framework Objectives: Clearly articulate the objectives of the data governance framework and its alignment with the organization’s data strategy. Identify the specific goals, principles, and guidelines that the framework will encompass.
- Assess Current State: Evaluate the existing data governance practices, data management processes, and data quality standards within the organization. Identify areas of improvement and gaps that need to be addressed by the framework. Understand the organization’s data ecosystem, including data sources, data flows, and data ownership.
- Design Framework Structure: Develop a structured framework that outlines data governance principles, roles, responsibilities, and processes. Consider industry best practices and incorporate regulatory and compliance requirements. Tailor the framework to the organization’s specific use cases, data management needs, and industry standards.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage key stakeholders across the organization to gather their input, align their expectations, and ensure their commitment to the framework. Collaborate with business units, IT teams, data owners, and data users to incorporate their perspectives and address their specific requirements. Foster a culture of data governance and ownership throughout the organization.
- Iterative Implementation: Implement the framework in iterative phases, focusing on specific use cases and scenarios. Collaborate closely with users to capture their feedback, address challenges, and refine the framework. Continuously improve the framework based on lessons learned and evolving data management practices.
- Training and Change Management: Provide comprehensive training programs to educate stakeholders and users about the framework’s principles, processes, and benefits. Plan for organizational change management to ensure smooth adoption and sustainment of the framework. Foster awareness, engagement, and support through communication, training, and ongoing support.
By following a structured methodology for system implementation and framework implementation, organizations can effectively execute their data strategies, drive meaningful change, and optimize their data management practices to gain a competitive advantage. Note: While this methodology draws upon best practices, it is essential to tailor the approach to each organization’s specific needs, capabilities, and industry requirements.
Conclusion
Implementing a data strategy is crucial for organizations to thrive in today’s business landscape. It offers numerous benefits, including improved decision-making, operational efficiency, and the ability to leverage data as a strategic asset. It’s beneficial to frame these implementations into two categories: System implementation and frameworks implementation. System implementation involves integrating new data technology solutions, such as data warehouses or business intelligence tools, to enhance data management processes and scalability, whereas, framework implementation introduces structured frameworks that streamline data governance practices and enable efficient data management, ensuring transparency, accessibility, and data quality. As you embark on implementing data strategy, it is important to plan for common complexities you might encounter such as change management, resource constraints, data quality, and system integration.
At Lionpoint, we offer valuable expertise and guidance to organizations seeking to transform their data operations. Our services include assisting in finding and launching the right enabling technologies, helping organizations navigate complexities, and tailoring methodologies to specific needs. Lionpoint provides support throughout the entire implementation process, from defining business objectives to evaluating and selecting solutions, planning and designing, configuring and developing, testing and quality assurance, and deployment and training. With Lionpoint’s comprehensive services, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data, drive meaningful change, and achieve their investment goals. Contact us today at mcastaneda@lionpointgroup.com to learn more or to schedule a consultation.