5 Key Elements of Data Management in Private Credit
August 23, 2023
Editor's Note: This post is the third in a four-part series titled "Unleashing the Power of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Building Your Private Markets Data Strategy" that explores the importance of having a data strategy framework for private markets and why it is a topic of growing interest, published by Lionpoint’s Front & Middle Office team.
Previous posts outlined the importance of formulating a target operating model, choosing a system, and assessing data frameworks. In this post, we will dive into the elements of executing a data strategy program, highlight the benefits of implementing a data strategy, identify common complexities of an implementation, and detail best-practice implementation elements and methodologies.
In the world of private credit, data has become an invaluable asset, shaping the landscape of investment decisions and risk assessment. As private credit experts, we recognize the crucial role that data management plays in achieving operational efficiency, making informed decisions, and unlocking new opportunities. In this article, we will explore 5 key elements of data management in private credit, highlighting common issues encountered within each, and examine how these can influence the performance and success of private markets firms.
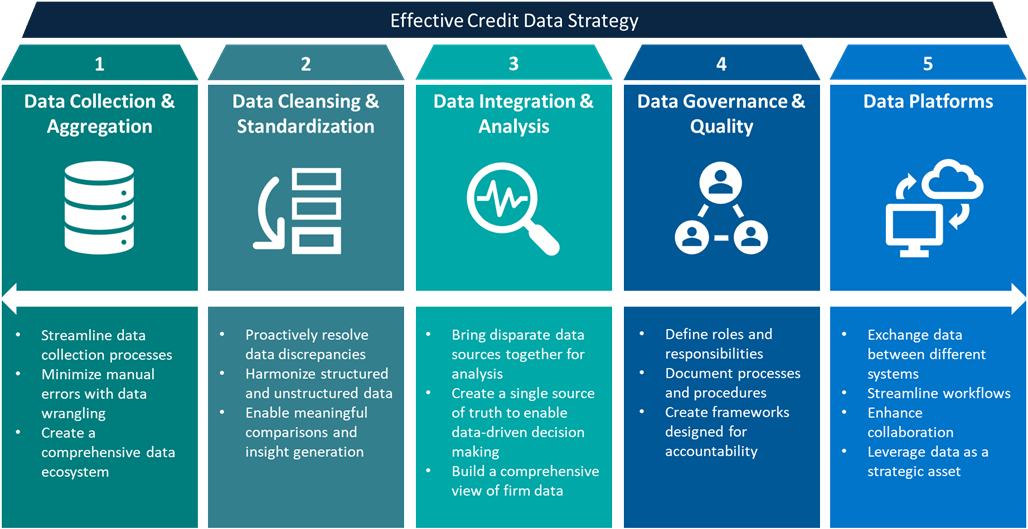
Data Collection and Aggregation:
The foundation of effective data management lies in robust data collection and aggregation processes. Numerous sources of structured and unstructured data exist in private credit, including borrower financials, deal and sector classifications, loan-level covenants, as well as market data, positional data, and security master data. The challenge lies in gathering these datasets from various sources, systems and stakeholders while ensuring data accuracy and completeness.
Common issues:
- Collecting financial data from borrowers who may use different accounting methods or have unique reporting structures.
- Receiving data in different document formats (such as PDF & Excel) which can make data extraction difficult.
- Combining financials from a wide geography of portfolio companies, as well as loan-level information from a variety of portfolio management systems.
- Monitoring various covenant limits to track breaches of credit agreements (an arduous task which can become an operational burden as the breadth and complexity of investments increase).
- Delays in collecting data across siloed data sources can create resource constraints and require manual intervention during reporting intensive periods such as quarter end.
Firms should look to leverage modern technologies such as automation, machine learning and optical character recognition (OCR) to streamline data collection, minimize manual input error, and create efficiency. Managers must collaborate with borrowers, investors, and other stakeholders to create a comprehensive data ecosystem and then layer on the right tool to bring this data together.
Data Cleansing and Standardization:
Data in private credit often contains discrepancies, errors, and inaccuracies. Successful data management demands rigorous data cleansing and standardization processes: identifying and resolving inconsistencies, formatting issues, missing values, and redundant entries.
Common issues:
- Standardizing credit data from different sources such as loan documents, financial statements and various point systems can be a time consuming and manual task for fund managers.
- The latest data is often not available for reporting or is incomplete to the point that it is unusable. This primarily impacts reporting accuracy and can have knock on impacts to compliance and covenant reporting at loan and asset levels.
Data cleansing is crucial as it harmonizes data across different sources, enabling seamless integration and analysis. Data standardization then enables meaningful comparisons, insights, and benchmarking to take place, all of which are needed to make informed business decisions.
Data Integration and Analysis:
The true power of data management is realized when various datasets are integrated and analysed holistically. Data integration enables a comprehensive view of borrowers’ financials, risk exposures, and market trends. Robust analytics tools facilitate data-driven insights, enabling private credit firms to make informed business and investment decisions.
Common issues:
- Data in private credit is increasing in volume and complexity. Creating an integrated view of this shifting data landscape is vital for scale and provides consistent asset-level data that can assist with forward-looking scenario analysis.
- The increasing demand from private credit investors for customized and ad-hoc portfolio reporting is seen as resource-intensive and difficult to put together. With the right data integration and analysis tools, these reporting requirements can be met with ease.
- A lack of data continuity and integration points across platforms and processes leads to duplicative work and potential inaccuracies in data.
From credit risk assessment to portfolio reporting, data-driven analysis enhances the effectiveness of private credit strategies by minimizing potential risks for fund managers. Consolidating data points from different sources can enable firms to create a single source of truth that empowers CFOs and COOs to make data-driven decisions with confidence.
Data Governance and Data Quality:
Maintaining data integrity is an ongoing process, and establishing robust data governance frameworks is critical. Data governance defines roles, responsibilities, and processes for data management, ensuring consistency and accountability across an organization.
Common issues:
- Creating data dictionaries, establishing data quality standards, and conducting regular audits to maintain data integrity.
- It is increasing difficult to maintain data quality over time, as new data sources are added and changes occur in the underlying systems such as migrations, upgrades, and vendor changes.
- Data quality degradation due to lack of internal controls and roles defined for maintaining and updating data.
Data governance introduces discipline, transparency, and rigor into the data management process to ensure continually high levels of data quality. Regular data quality assessments and audits are vital to maintaining high data standards. By continuously monitoring data quality, private credit firms can identify and rectify issues promptly, and prevent errors from spreading.
Data Platforms
A good data platform provides an organization with the infrastructure to process and analyze data more effectively. This is significant for private credit firms who have traditionally relied on excel spreadsheets and manual workflows to bring data together from different sources. By transitioning to a robust platform, organizations can experience immediate improvements in their data management processes. With the right platforms in place, efficiency can increase, costs can be reduced, and risks associated with data management can be mitigated.
Common issues:
- Private credit firms often have data spread across multiple systems and applications, making it difficult to gain a comprehensive view of their business in one place.
- As investment complexity increases, fund managers require technology that can handle large volumes of credit data to support advanced analytics.
- Automation of quarterly reports – combining positional, credit, and financial data for reporting is often a manual and time-consuming process spanning multiple business groups and disparate data sources.
A robust data platform can enable scale across the credit data lifecycle – from deal origination to closing – and simplifies ongoing loan management and portfolio monitoring. Data platforms facilitate the seamless exchange of data with internal and external systems and between stakeholders, streamlining workflows and enhancing collaboration across a firm. With normalized data aggregated and readily available, private credit professionals can make well-informed decisions with greater agility, drive operational efficiencies, and leverage the full potential of their data sources.
Conclusion:
Data management is the backbone of success in the world of private credit. By taking a holistic approach to a data strategy and incorporating each of these elements, firms can gain valuable insights, make informed business decisions, and mitigate risks effectively in an increasingly data-centric environment. Understanding the nuances of data management can help private credit firms achieve new heights of success and contribute to growth, resilience, and long-term competitive advantage.